NSERC Funded SAP MRS Technician
NSERC Subatomic Physics Major Resource Support University of Winnipeg detector mechanics and electronics
Resource capabilities
This NSERC SAP MRS supports the technician Shomi Ahmed, who holds a BSc in electrical & electronics engineering, and MSc in experimental particle physics. Shomi is an engineer in training in Manitoba, and is being mentored through the TRIUMF engineering mentoring program with the goal of becoming a professional engineer. Since starting at the University of Winnipeg in Fall 2020, Shomi has provided technical support mainly to the Hyper-Kamiokande project, and to the TUCAN ultracold neutron project. Shomi is currently working on camera readout electronics for the Hyper-K photogrammetry underwater cameras, with connections up to 100 m. For TUCAN, Shomi is working on:
- a 7-channel relay-contactor board for the magnetically shielded room's degaussing system,
- a high stability current source (~1 ppm / hour) for the nEDM holding magnetic field coils, and
- a 50-channel bipolar current source for nEDM shim coils
The University of Winnipeg has a small clean room for detector fabrication, three small Prussa 3D printers, and a larger 0.5x0.5x0.5 m 3D printer, and a small machine shop for small jobs. The technician will have access to fabrication facilities at North Forge (https://www.northforge.ca). At North Forge the technician has access to additional 3D printers, CNC machines, laser cutters, and PCB layout and stuffing equipment. Shomi has been working with students carrying out experiments at the University of Winnipeg for the last two years, and is excellent at working with and training students in hands-on projects safely. HQP working with Shomi have gained valuable skills in laying out PCB boards, in fabrication, computer aided design, in instrumentation, and in programming in python. Shomi likes to get things built, and works with any HQP interested in bringing their experiment into operation.
Examples of previous projects
Figure 1 shows the camera readout electronics connection for Hyper-K photogrammetry. HDMI extender will provide lag free live feed whereas USB extender will be used to communicate with the underwater cameras. The extenders will support up to 100 meters of ethernet cable and the power over ethernet (PoE) has been used to reduce the number of feedthroughs on camera housing.
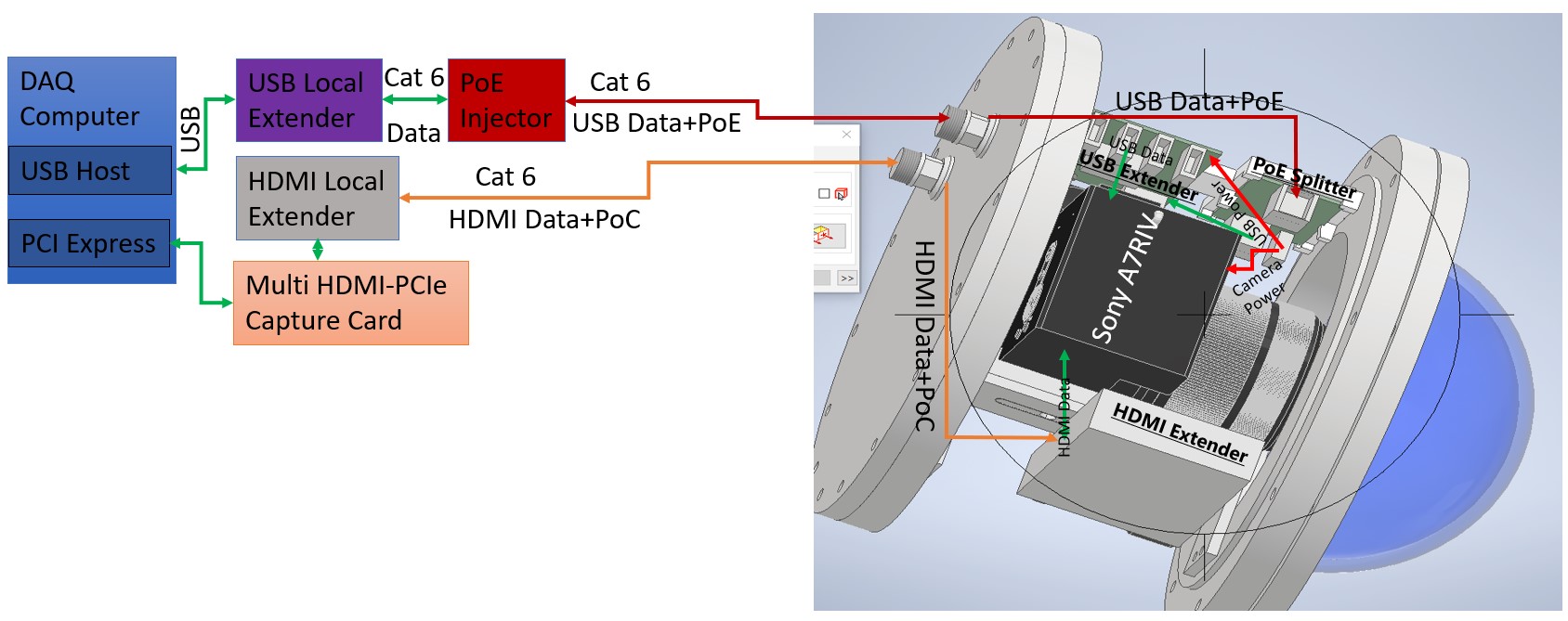
Fig. 2 shows the camera under water with the electronics connection. The camera was under water for 9 days and we have not observed any leakage or power failure in the camera.
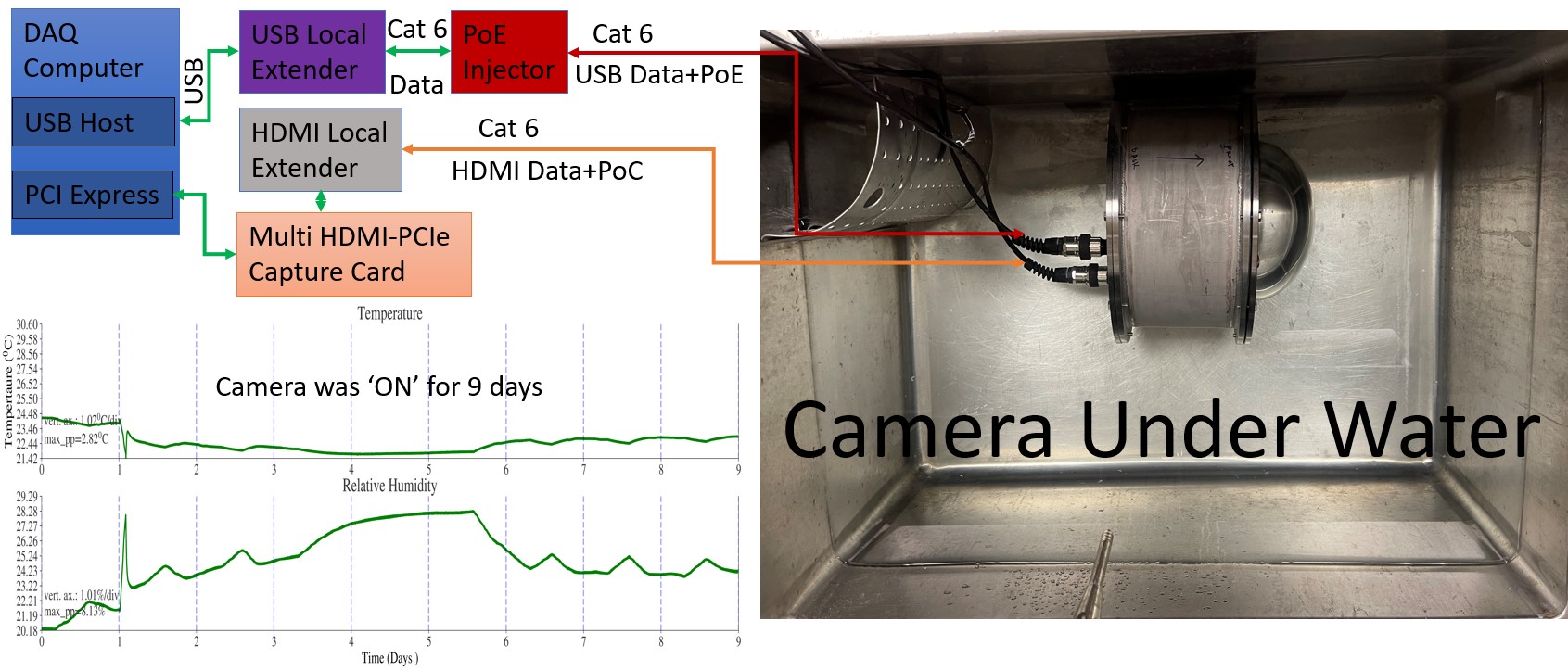
Fig. 3 shows the PC-side connection for 8-Cameras. The workstation, extenders, poe injector etc. are placed in the rack.
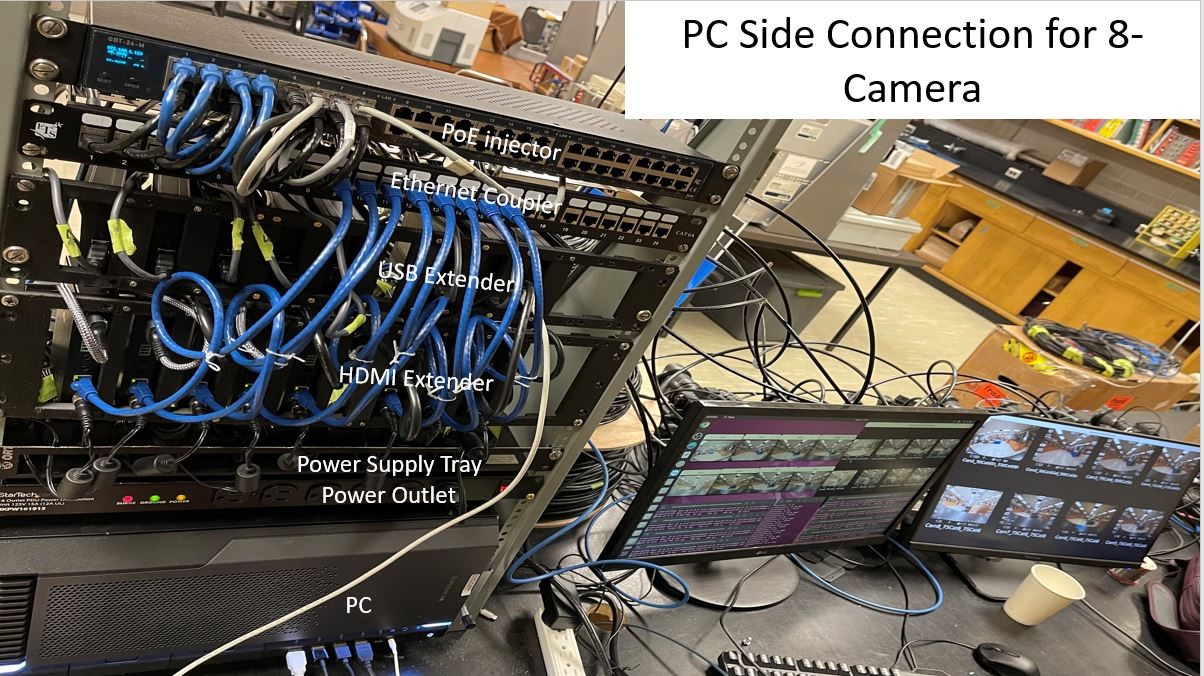
Fig.4 shows the live feed via HDMI extender from 8-cameras

Fig. 5 shows the block diagram of a relay-contactor board for the magnetically shielded room's degaussing system.
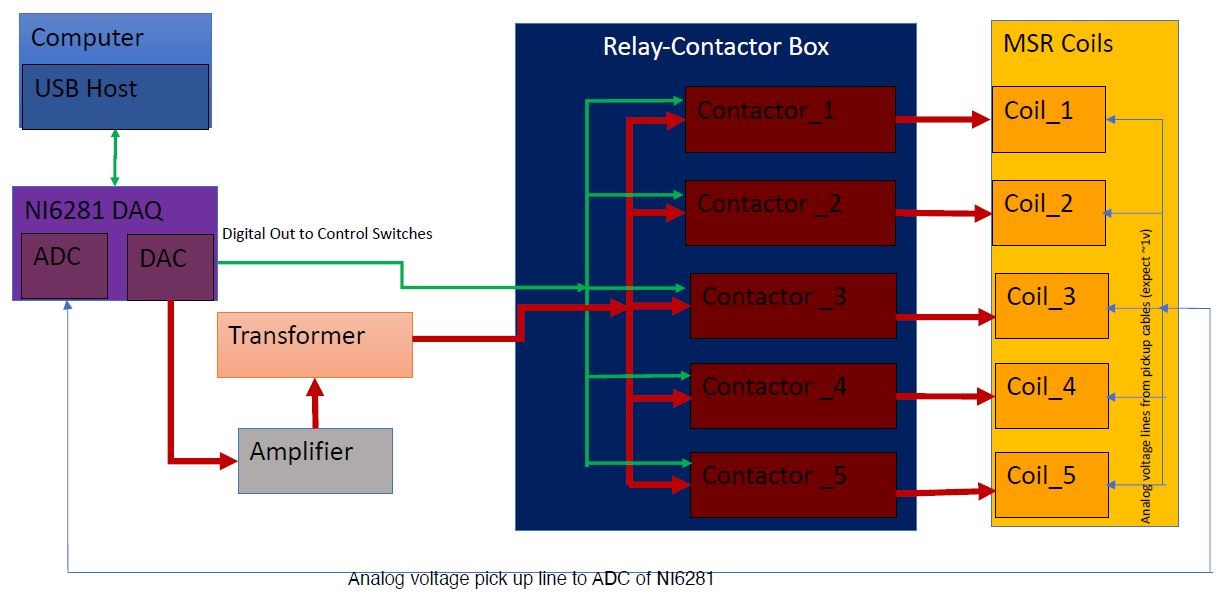
Fig. 6 shows the complete 7-channel relay-contactor panel board. Shomi has planned the design and executed.
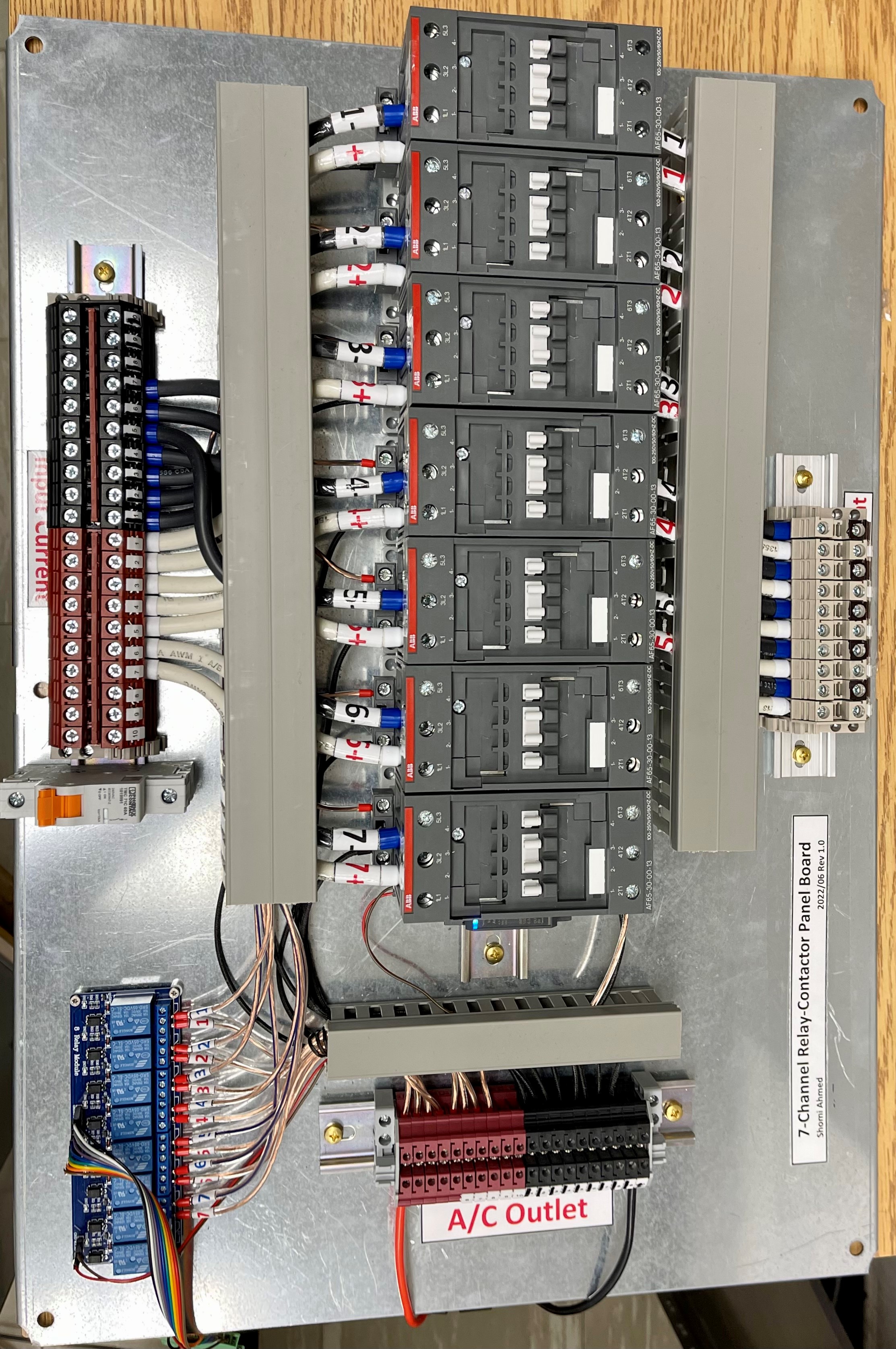
Fig. 7 shows simulating different precision current supplies in LTSpice to determine the best stable current supplies for B0 coil in TUCAN project.
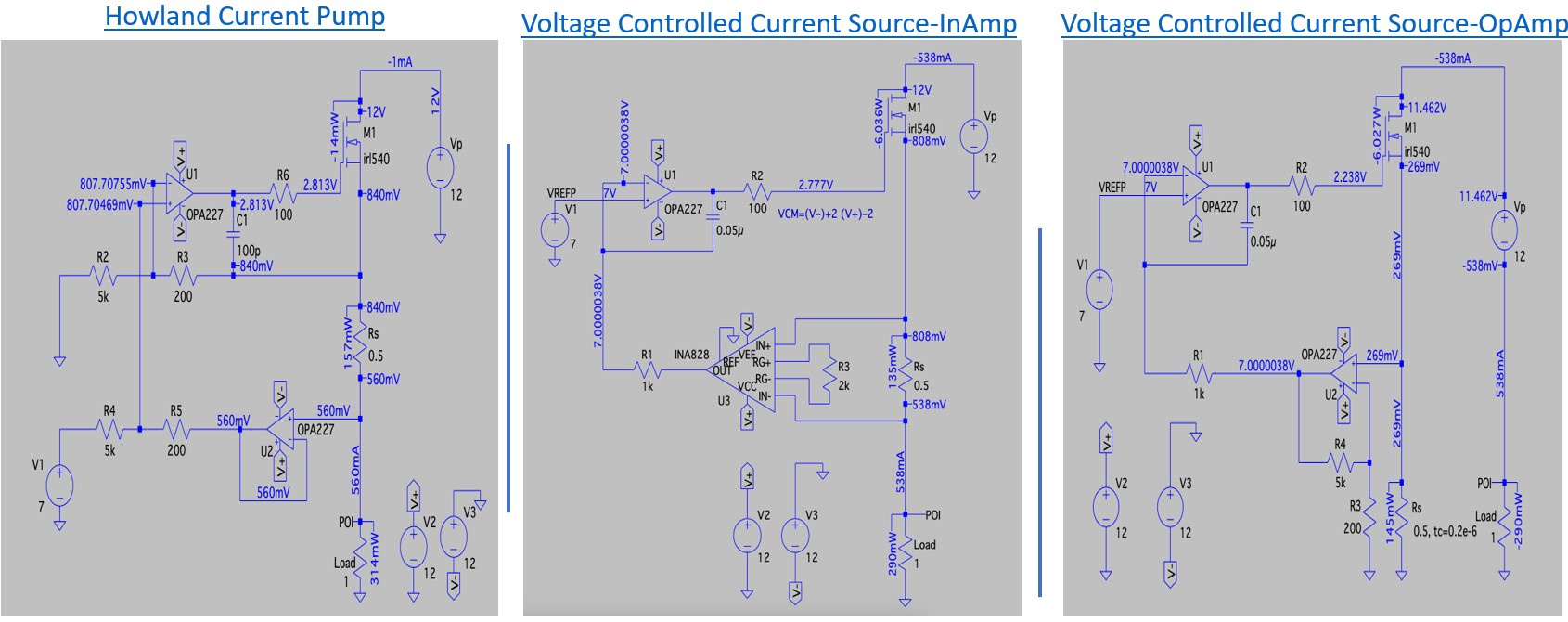
Fig. 8 shows the different sub-modules that Shomi built for the current supply.
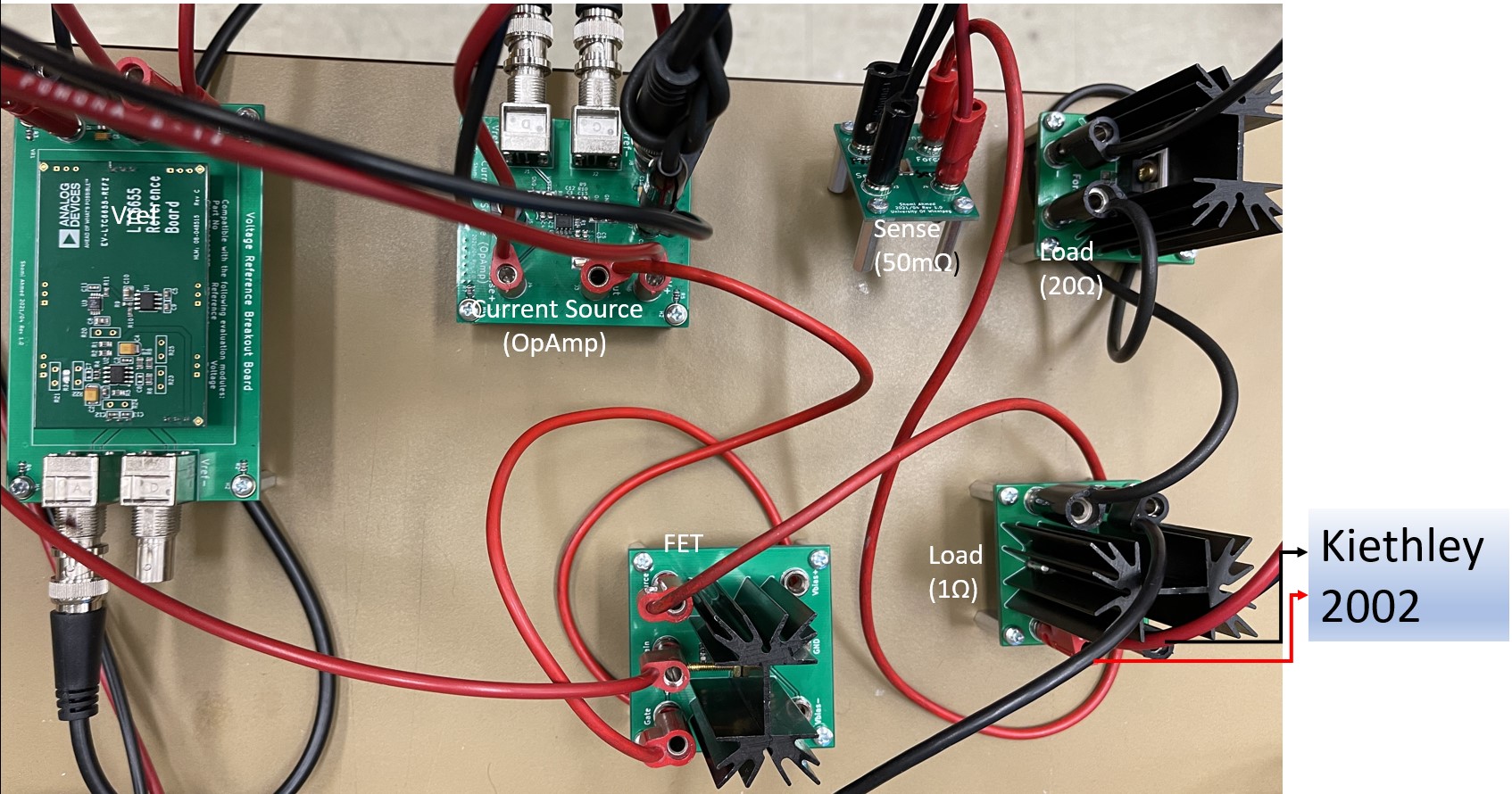
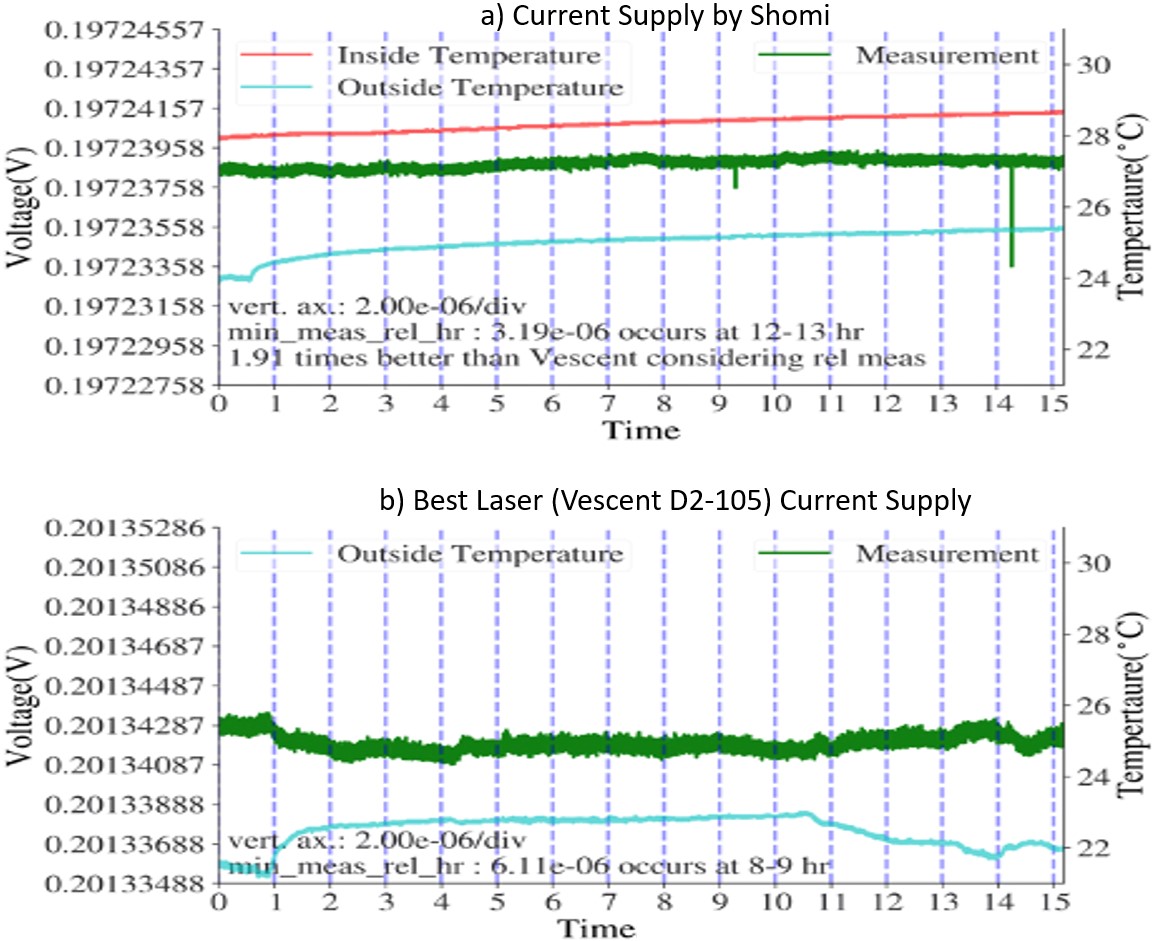
Fig. 9 shows the comparison between a) the current supply by Shomi and b) best laser current supply. Shomi’s current supply shows ~2 times better than the laser current supply. Moreover, other studies show that Shomi’s supply is ~10 and ~140 times better than Agilent and Rigol current supplies respectively. Moreover, Shomi’s current supply is not limited by small compliance voltage and hence limited load resistances (no suitable for TUCAN B0 coil) unlike all other current supplies.
How to request support from this MRS resource
This MRS resource is available to the subatomic physics community. Many of the projects Ostapchuk has worked on already have been in support of national projects. This resource is managed by the University of Winnipeg, University of Victoria, and Carleton MRS resource allocation board.
To request the use of these resource, please fill in the form here, to describe the project scope and send it to: bl.jamieson@uwinnipeg.ca.
You can find more information about the different MRS resource sites from the Canadian Institute of Nuclear Physics (CINP) and Institute for Particle Physics (IPP) sites.
